While contribution margins only count the variable costs, the gross profit margin includes all of the costs that a company incurs in order to make sales. The contribution margin is the foundation for break-even analysis used in the overall cost and sales price planning for products. xero community With a contribution margin of $200,000, the company is making enough money to cover its fixed costs of $160,000, with $40,000 left over in profit. To convert the contribution margin into the contribution margin ratio, we’ll divide the contribution margin by the sales revenue.
Formula For Contribution Margin
It represents the incremental money generated for each product/unit sold after deducting the variable portion of the firm’s costs. The contribution margin (CM) is the profit generated once variable costs have been deducted from revenue. Assuming factors like demand and competition are equal, the company should make the product with the highest return relative to variable costs in order to maximize profits. Conceptually, the contribution margin ratio reveals essential information about a manager’s ability to control costs. So, for example, you could calculate contribution margin ratio annually for a broad view into the impact of changes to sales, or calculate it on a single sale for a precise view into how your business is running. When preparing to calculate contribution margin ratio, you will need to add together all of your variable expenses into one number.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
Understanding how each product, good, or service contributes to the organization’s profitability allows managers to make decisions such as which product lines they should expand or which might be discontinued. When allocating scarce resources, the contribution margin will help them focus on those products or services with the highest margin, thereby maximizing profits. It is important to note that this unit contribution margin can be calculated either in dollars or as a percentage.
- If the company realizes a level of activity of more than 3,000 units, a profit will result; if less, a loss will be incurred.
- However, the contribution margin ratio won’t paint a complete picture of overall product or company profitability.
- If you need to estimate how much of your business’s revenues will be available to cover the fixed expenses after dealing with the variable costs, this calculator is the perfect tool for you.
- Investors often look at contribution margin as part of financial analysis to evaluate the company’s health and velocity.
- You can use the contribution margin calculator using either actual units sold or the projected units to be sold.
Calculate Contribution Margin Ratio
Other reasons include being a leader in the use of innovation and improving efficiencies. If a company uses the latest technology, such as online ordering and delivery, this may help the company attract a new type of customer or create loyalty with longstanding customers. In addition, although fixed costs are riskier because they exist regardless of the sales level, once those fixed costs are met, profits grow. All of these new trends result in changes in the composition of fixed and variable costs for a company and it is this composition that helps determine a company’s profit. The break even point (BEP) is the number of units at which total revenue (selling price per unit) equals total cost (fixed costs + variable cost). If the selling price per unit is more than the variable cost, it will be a profitable venture otherwise it will result in loss.
How to Calculate Contribution Margin?
All you have to do is multiply both the selling price per unit and the variable costs per unit by the number of units you sell, and then subtract the total variable costs from the total selling revenue. Let’s examine how all three approaches convey the same financial performance, although represented somewhat differently. As mentioned above, contribution margin refers to the difference between sales revenue and variable costs of producing goods or services.
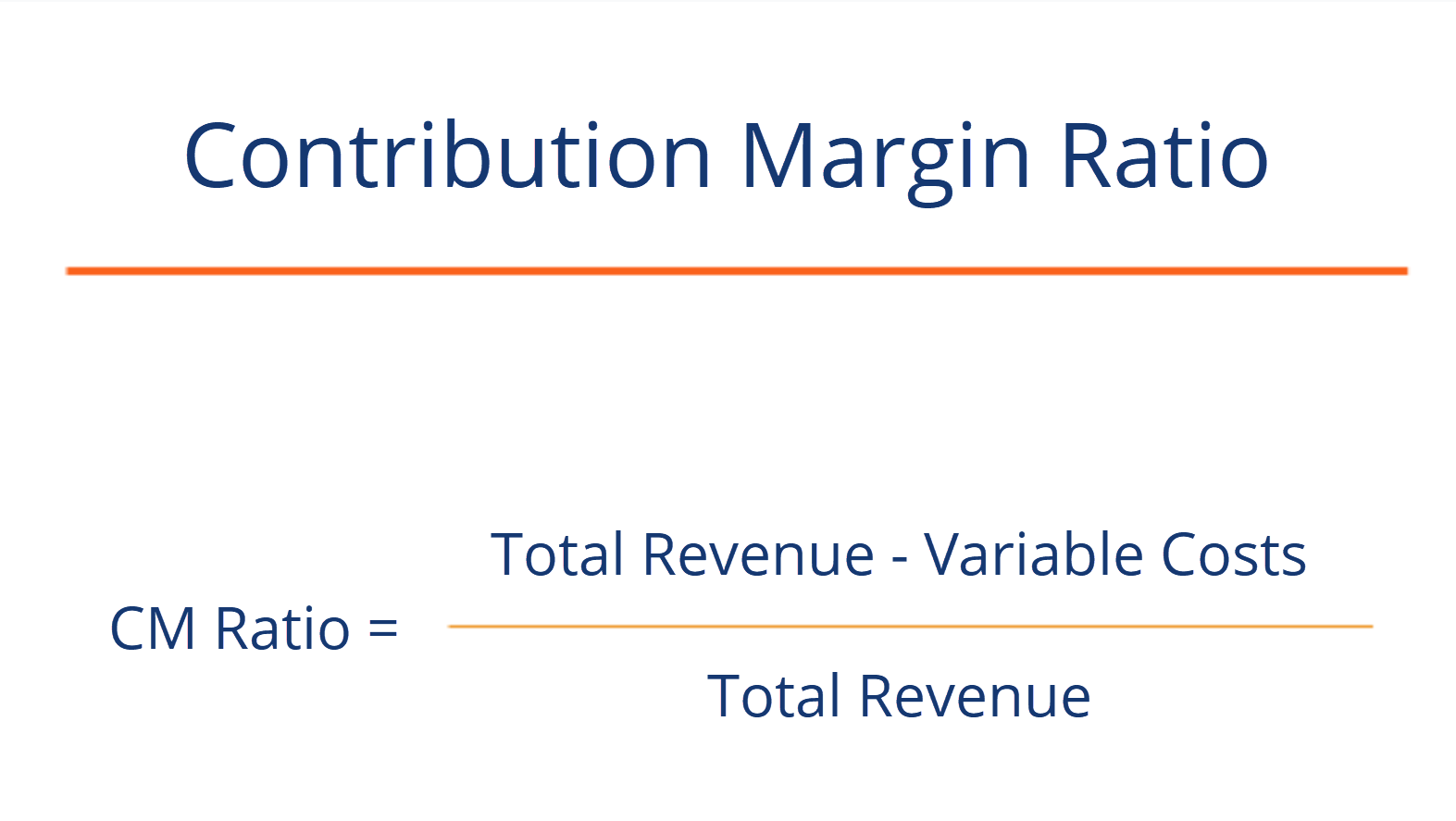
You can use it to learn how to calculate contribution margin, provided you know the selling price per unit, the variable cost per unit, and the number of units you produce. The calculator will not only calculate the margin itself but will also return the contribution margin ratio. For the month of April, sales from the Blue Jay Model contributed \(\$36,000\) toward fixed costs. The Contribution Margin Ratio is a measure of profitability that indicates how much each sales dollar contributes to covering fixed costs and producing profits. It is calculated by dividing the contribution margin per unit by the selling price per unit. The contribution margin ratio is a formula that calculates the percentage of contribution margin (fixed expenses, or sales minus variable expenses) relative to net sales, put into percentage terms.
Once the $31,000 has been covered, 70% of the revenues will flow to the company’s net income. As you will learn in future chapters, in order for businesses to remain profitable, it is important for managers to understand how to measure and manage fixed and variable costs for decision-making. In this chapter, we begin examining the relationship among sales volume, fixed costs, variable costs, and profit in decision-making. We will discuss how to use the concepts of fixed and variable costs and their relationship to profit to determine the sales needed to break even or to reach a desired profit. You will also learn how to plan for changes in selling price or costs, whether a single product, multiple products, or services are involved. For the month of April, sales from the Blue Jay Model contributed $36,000 toward fixed costs.
Net sales are basically total sales less any returns or allowances. This is the net amount that the company expects to receive from its total sales. Some income statements report net sales as the only sales figure, while others actually report total sales and make deductions for returns and allowances. Either way, this number will be reported at the top of the income statement. Sales (a.k.a. total sales or revenue) is the monetary value of the goods or services sold by your business during a certain reporting period (e.g., quarterly or annually).